
Network performance assessment is a critical task for system administrators. System admins are often required to master more than one Linux network monitor tools because every tools offer something unique to the system analysis. There are plenty of Linux network monitoring tools out there. Although each tool has different scope for usage, learning about most of them can be useful. It is essential as an system admin to find unauthorized usage of network resources.
Linux network monitor tools
Speedometer
This tool gives you graphical representation of your network speed. You can see your network’s up and down stream or RX and TX speed. Which essentially gives you speed at which data coming and going out of your Linux machine. Now to use the speedometer use the following command.
#speedometer -r eth0 -t eth0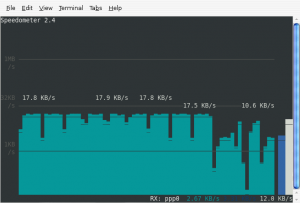
-R option is for your receiving interface on which your internet is working
-T option is for your transmitting interface which is also same as receiving interface.
After issuing the above mentioned command, you can see the RX and TX speed in graphical manner which is pretty handy if you want a quick glance or snapshot of your network usage overtime.
Installation
On Debian or Debian based distros like , Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Kali etc.
sudo apt-get install speedometer
Installation on Arch or Arch based system like Manjaro, AntergOS, BlackArch etc.
#yay -Syy speedometer
For any other Linux distro, you can download the source from github and compile it locally.
iftop
Next is iftop on the list. It’s very popular among system admins. iftop is a free and open source program. One of the best Command-line Linux network monitoring tool that produces a frequently updated list of network connections. By default, the connections are listed by bandwidth usage, starting from “top” bandwidth consuming process. To use iftop use the following command with root privileges.
#sudo iftop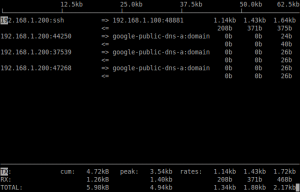
After issuing the commands, Terminal screen will give you a real time information about all the incoming and outgoing network traffic on your computer. First column shows the source address and second column shows the destination address. Three columns on the right hand side shows the data sent in past two seconds, 10 seconds and 40 seconds respectively. There are few more option available, pressing the H key takes you to the health menu which shows you all the options available.
SS – Socket Statistics
This Linux Network monitor tool is similar to netstat but a lot simpler and faster. Typing ss on CLI interface gives you a lot of information which is pretty hard to comprehend. So following options are recommend to use with SS for more easily understandable output. SS usally comes per-installed with most major distros.
#ss -l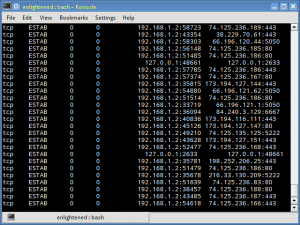
Command used above gives you list of all listening sockets.
-t option gives you list of all the TCP connection which is currently established. Similarly, -u option gives you the list of UDP connection.
One more usefull option is dst.
#ss dst ipaddress
This will show you the information, how a particulate IP is connected to your network. Which is pretty handy if you are investigating a specific IP address.
IPTraf
The IPTraf Linux network monitor is an ncurses-based IP LAN monitor (so it’s text-based) that is interactive and generates network statistics such as: TCP info, UDP counts, ICMP and OSPF information, Ethernet load info, node stats, IP checksum errors, and more.
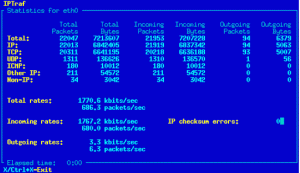
Now, the only problem with IPTraf is that it is old. It hasn’t been updated since 2005 (as far as I can see). It may be old but it’s far from being useless. The iptraf tool still installs, still runs, and is just as useful as it was when it was still in active development. It provides multiple options to filter your network traffic.
Installation
On RHEL, CentOS and Fedora server using yum command from terminal.
#yum install iptraf
Under Debian or Ubuntu, IPTraf can be installed by
#sudo apt-get install iptraf
On Arch or Arch based systems
#sudo pacman -S iptraf-ngNetHogs – Monitor Per Process Network Bandwidth
NetHogs is an open source piece of program (similar to Linux top command). It tracks each process’s network activity on your Linux system. It also helps you finding the real-time network traffic bandwidth usage by each program or application. Nethogs is interactive in nature. It uses the ncurses library. It expects to launch in a terminal window and get input from the user, there’s no GUI for the program.
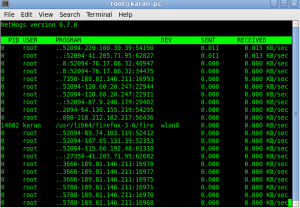
Instead of dividing down the traffic per protocol or per subnet, like most of such Linux network monitor do, it groups bandwidth by process – and It does not require any special kernel module to be loaded. So if there’s sudden spike in network usage, you can fire up NetHogs and immediately see which PID is causing this, and if it’s some kind of spinning process, kill it.
Installation
On Rad-Hat and CentOS based systems
#yum install nethogs
On Debian and Ubuntu
#sudo apt-get install nethogs
On Arch or Arch based systems
#sudo pacman -S nethogsNetstat
Netstat is basically a command line Linux network monitor tool which list out all the network connection established by processes running on your system. It mainly lists out all the UDP, TCP socket connections and also the Unix socket connection. Not only sockets it can also easily list the listening sockets that are actually waiting for the incoming connections, so it would be good if you check that the open port 80(http) is running on the system or not. Mostly it comes per-installed with your Linux distro, it is a very useful tool for the network and the system administrators.
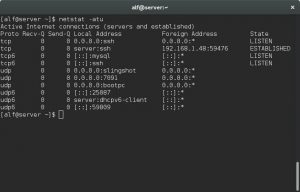
If you don’t have net-tools installed on your system, which provides Netstat, you can install it by following commands:
yum install net-toolsapt install net-toolspacman -S netstat-natnload – Displays Network Usage
nload is a another very good piece of program, nload is very easy to use command-line tool for inspecting network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time. It uses graphs to visualize the incomming and outgoing traffic. In addition, it also displays information such as the total amount of transferred data and minimum and maximum network usage.
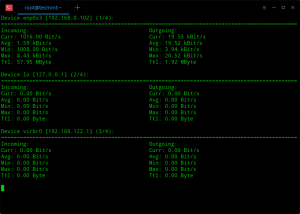
Installation
On Red-Hat and CentOS based systems
yum install nload
On Debian
sudo apt-get install nload
On Arch
sudo pacman -S nload
That’s our top picks for Linux network monitor tools, if you feel otherwise please let us know in the comments.

Post a Comment